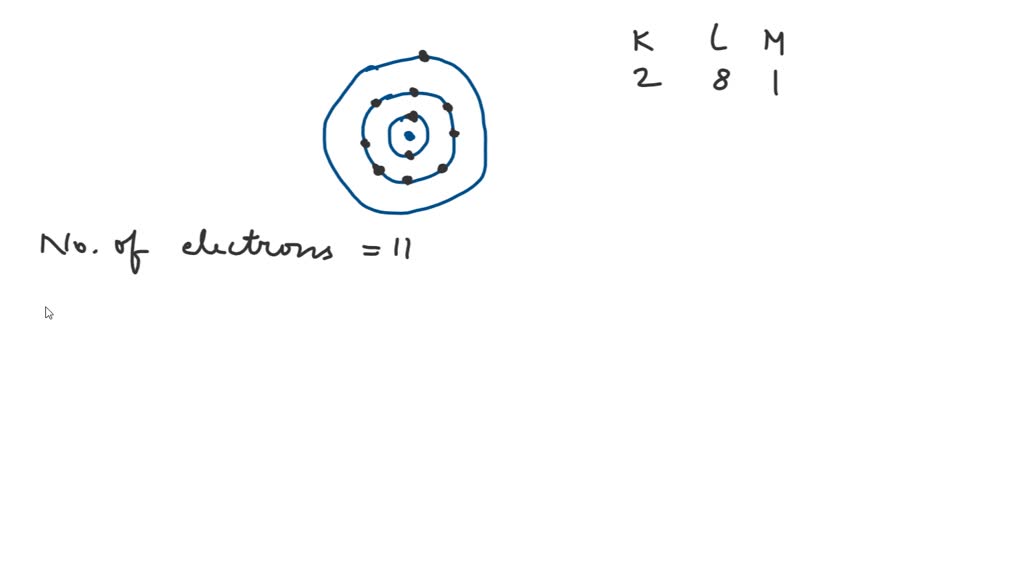
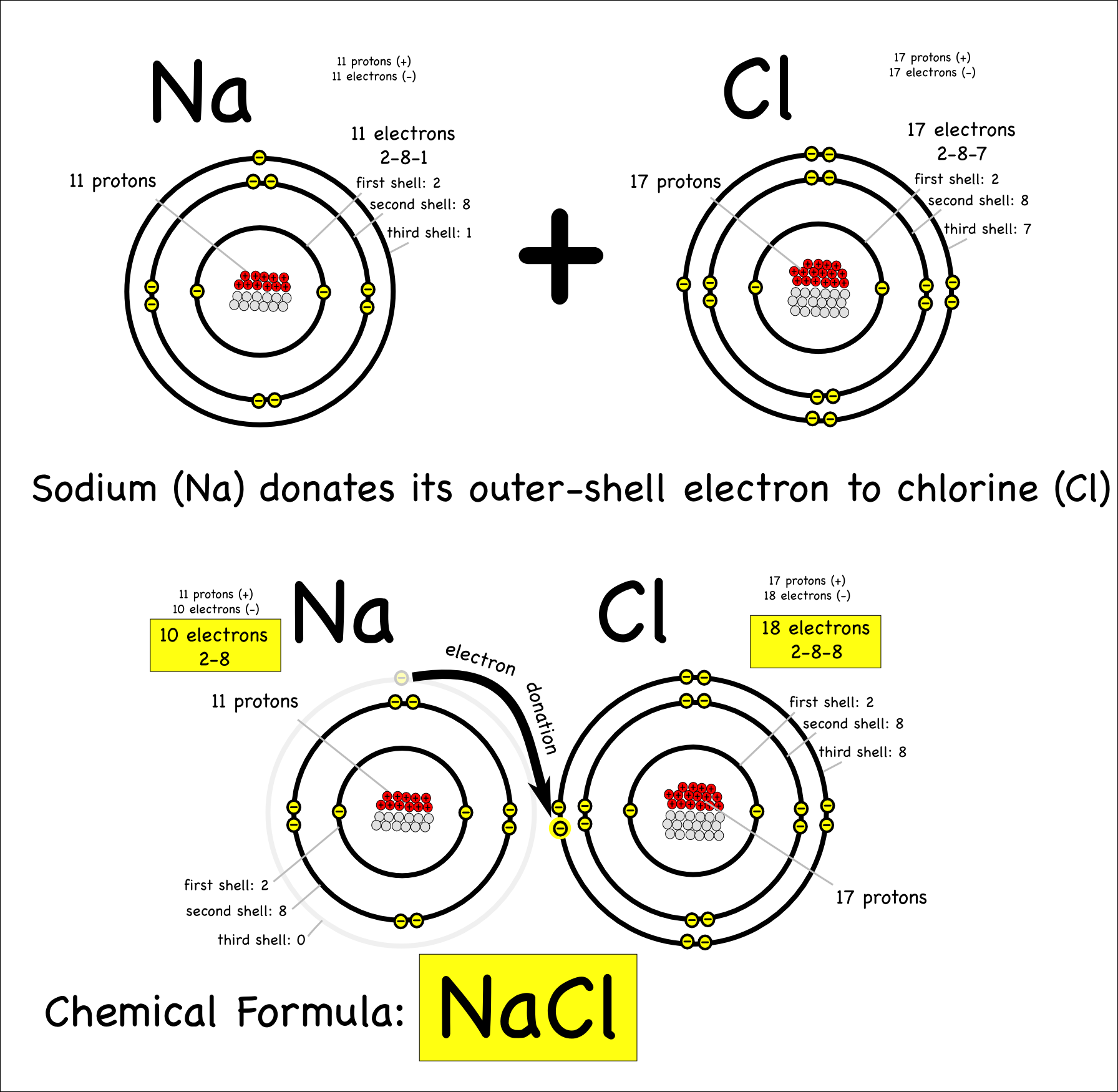
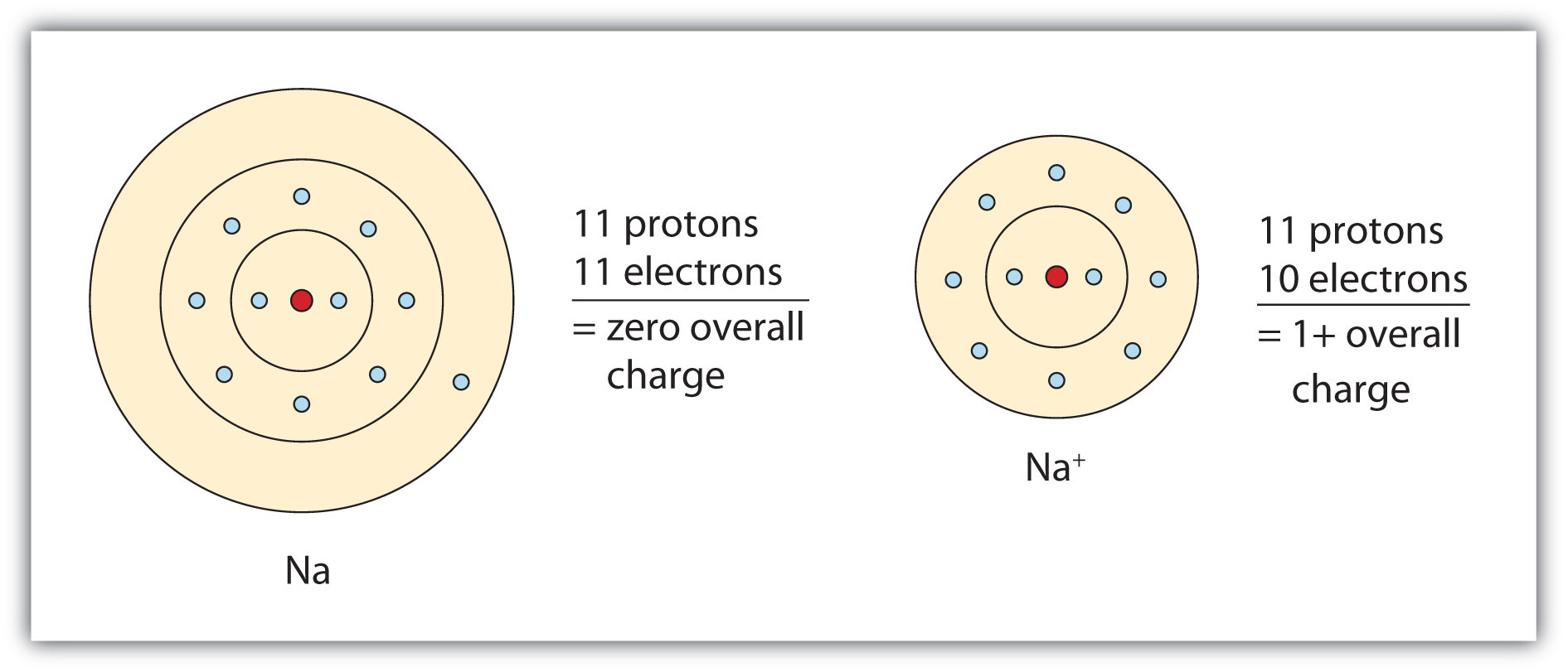
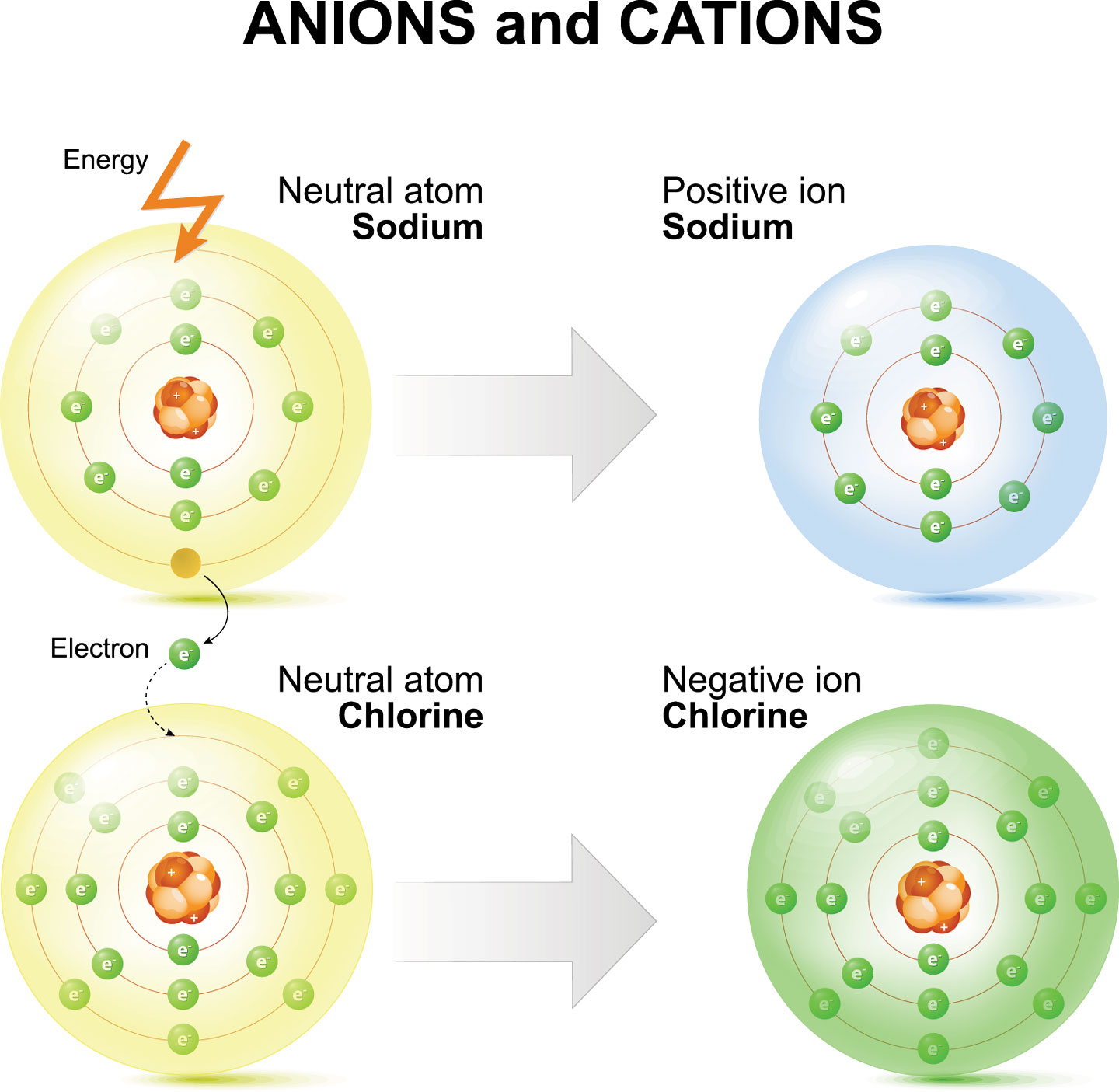
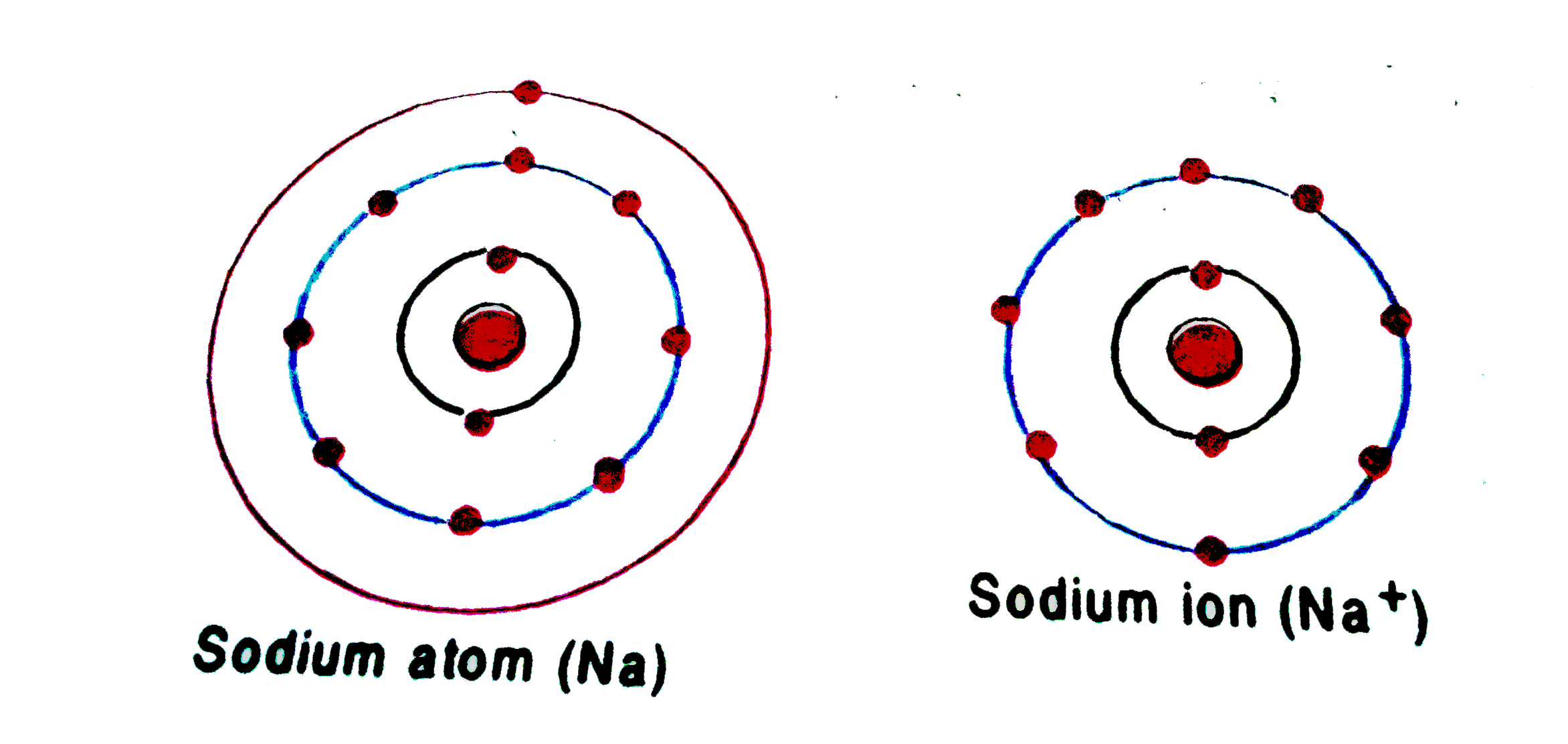
Sodium Forms An Ion With A Charge Of - Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium ion still has. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium.
The sodium ion still has. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. Well, we form a na^+ ion. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Sodium metal is easily oxidized.
Sodium metal is easily oxidized. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium ion still has. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge.
Sodium Forms an Ion With a Charge of JasminehasGillespie
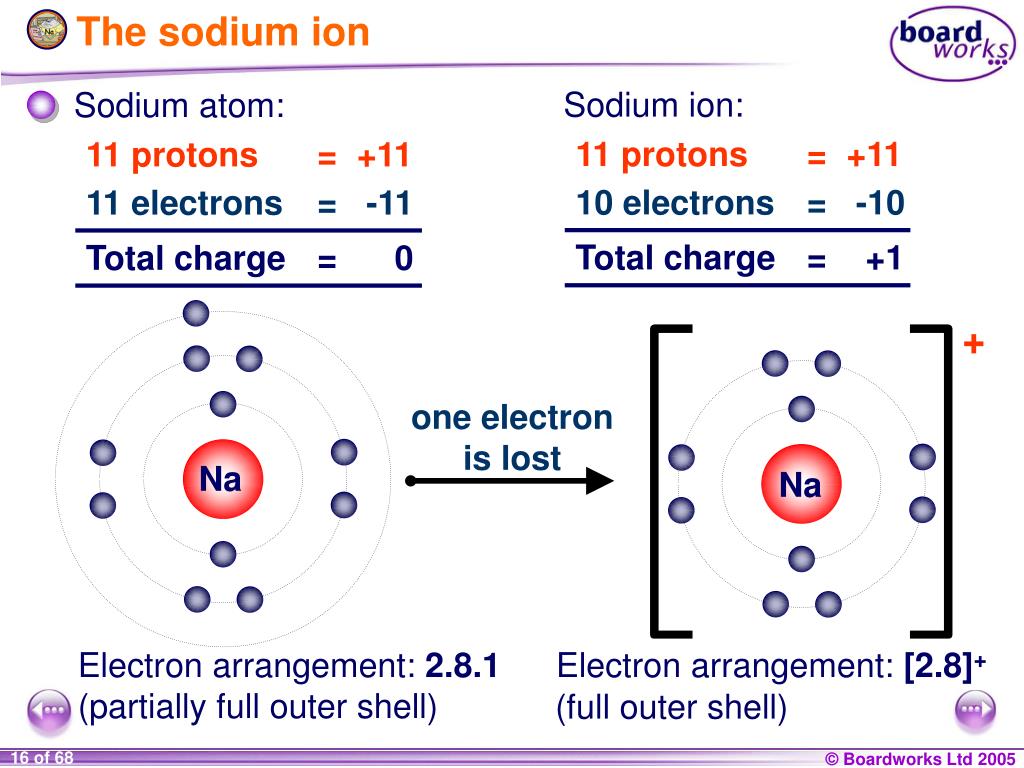
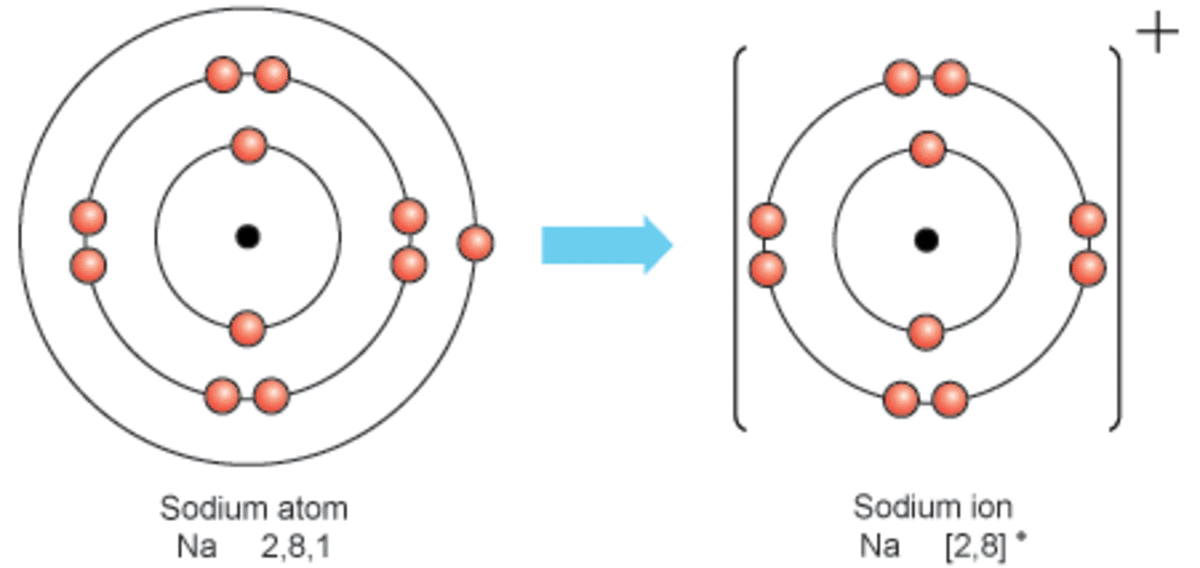
The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium ion still has. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium.
SOLVED Sodium has 11 electrons arranged in three energy levels. In
When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. The sodium ion still has.
PPT KS4 Chemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5413898
Sodium metal is easily oxidized. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium ion still has.
Sodium Electron Configuration (Na) with Orbital Diagram
The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. The sodium ion still has. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Sodium metal is easily oxidized.
Chemical Bonding How Do Atoms Combine? What Are the Forces That Bind
When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium ion still has. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion.
subatomic particles Montessori Muddle
Sodium metal is easily oxidized. The sodium ion still has. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium.
Ions
Well, we form a na^+ ion. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The sodium ion still has.
Explainer Ions and radicals in our world Science News for Students
The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. The sodium ion still has.
Sodium Electron Configuration Electron Configuration Sodium What is
For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. Sodium metal is easily oxidized. Well, we form a na^+ ion. The sodium ion still has. When sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge.
When Sodium Atoms Form Ions, They Always Form A 1+ Charge, Never A 2+ Or 3+ Or Even 1− Charge.
For example, in the compound sodium chloride — table salt — the sodium. The sodium atom loses its outer electron to become a sodium ion. The sodium ion still has. Well, we form a na^+ ion.