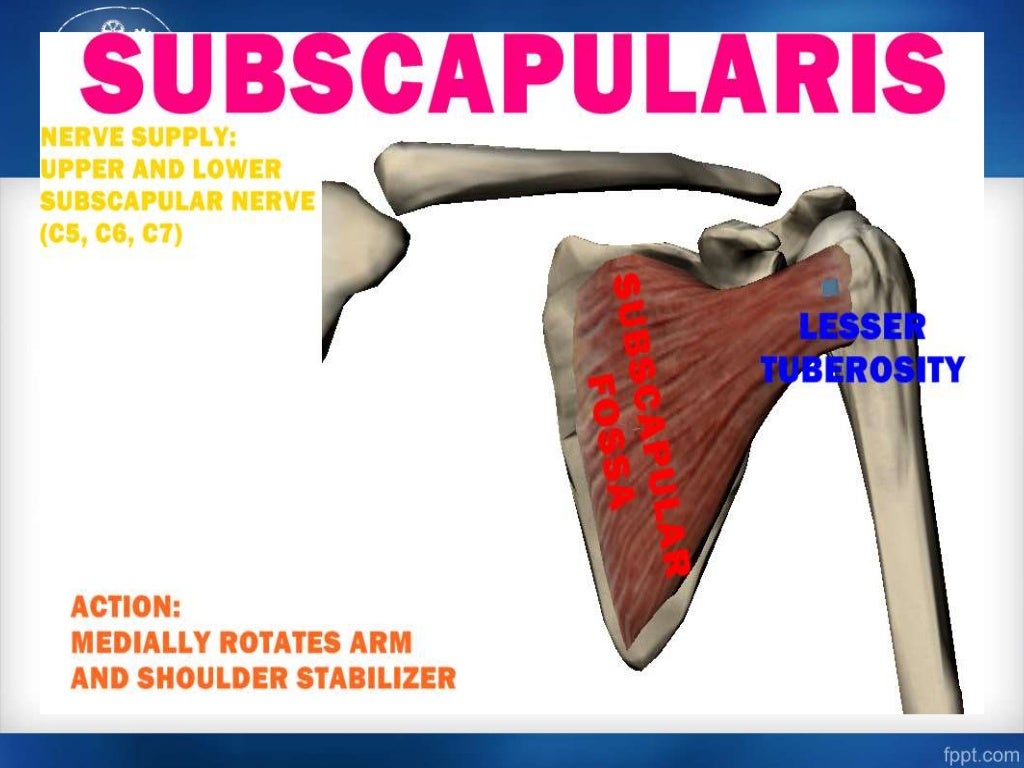
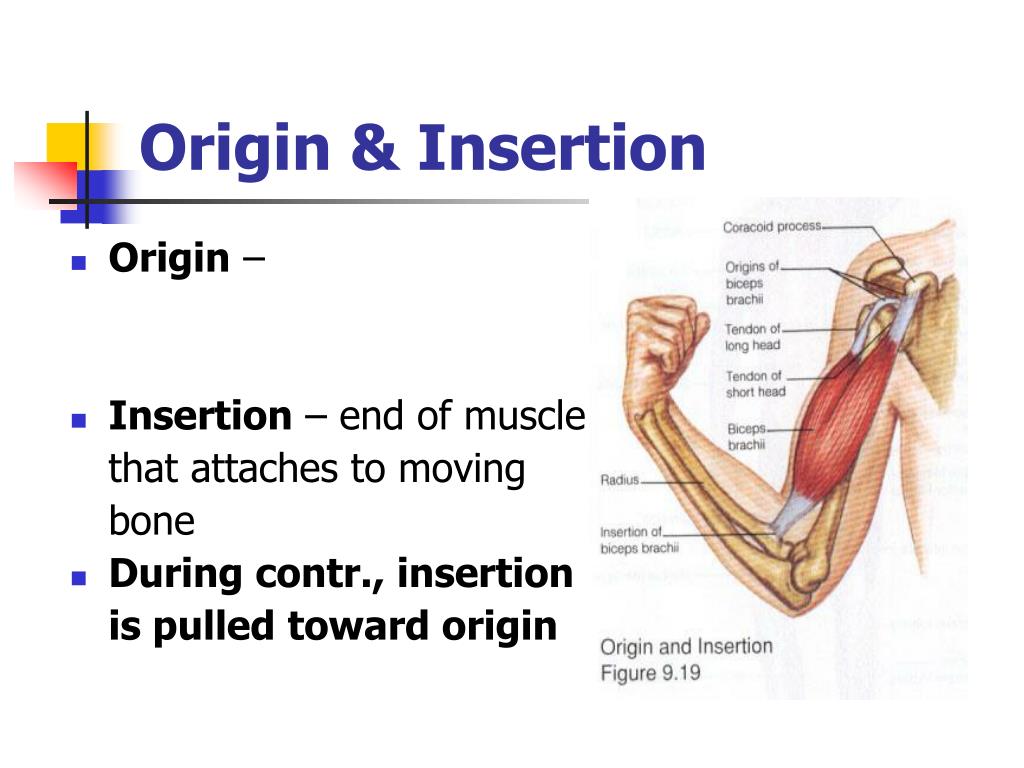
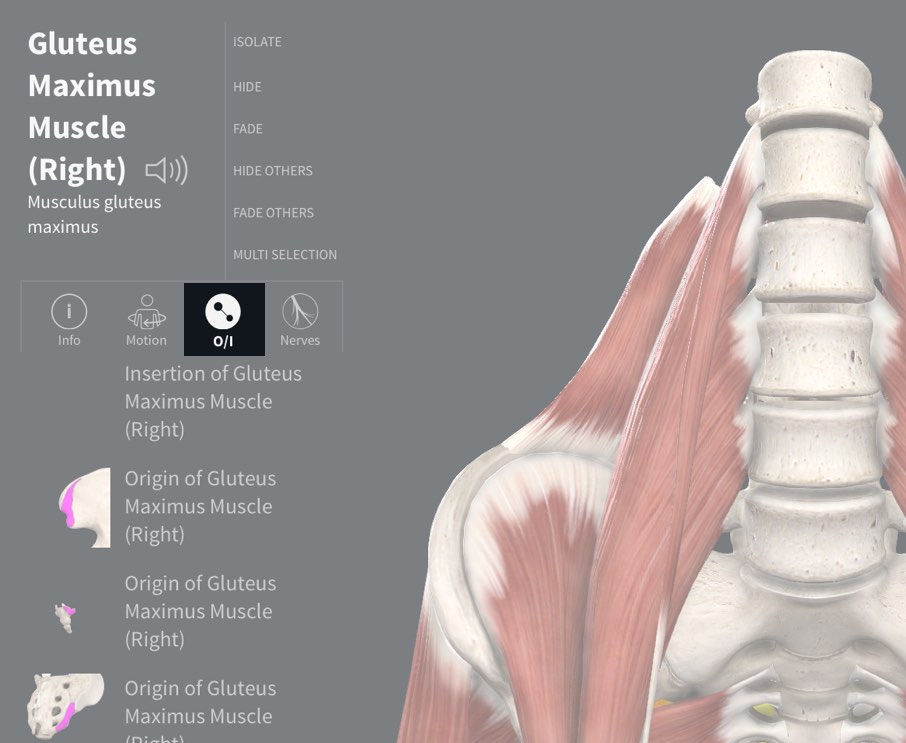
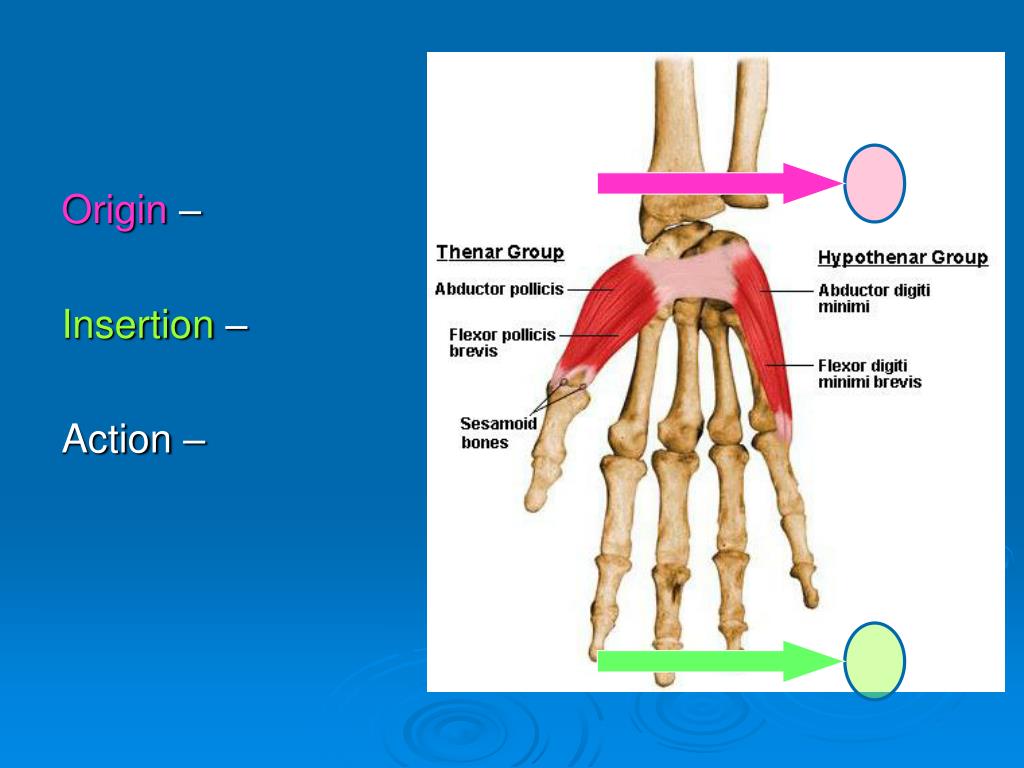
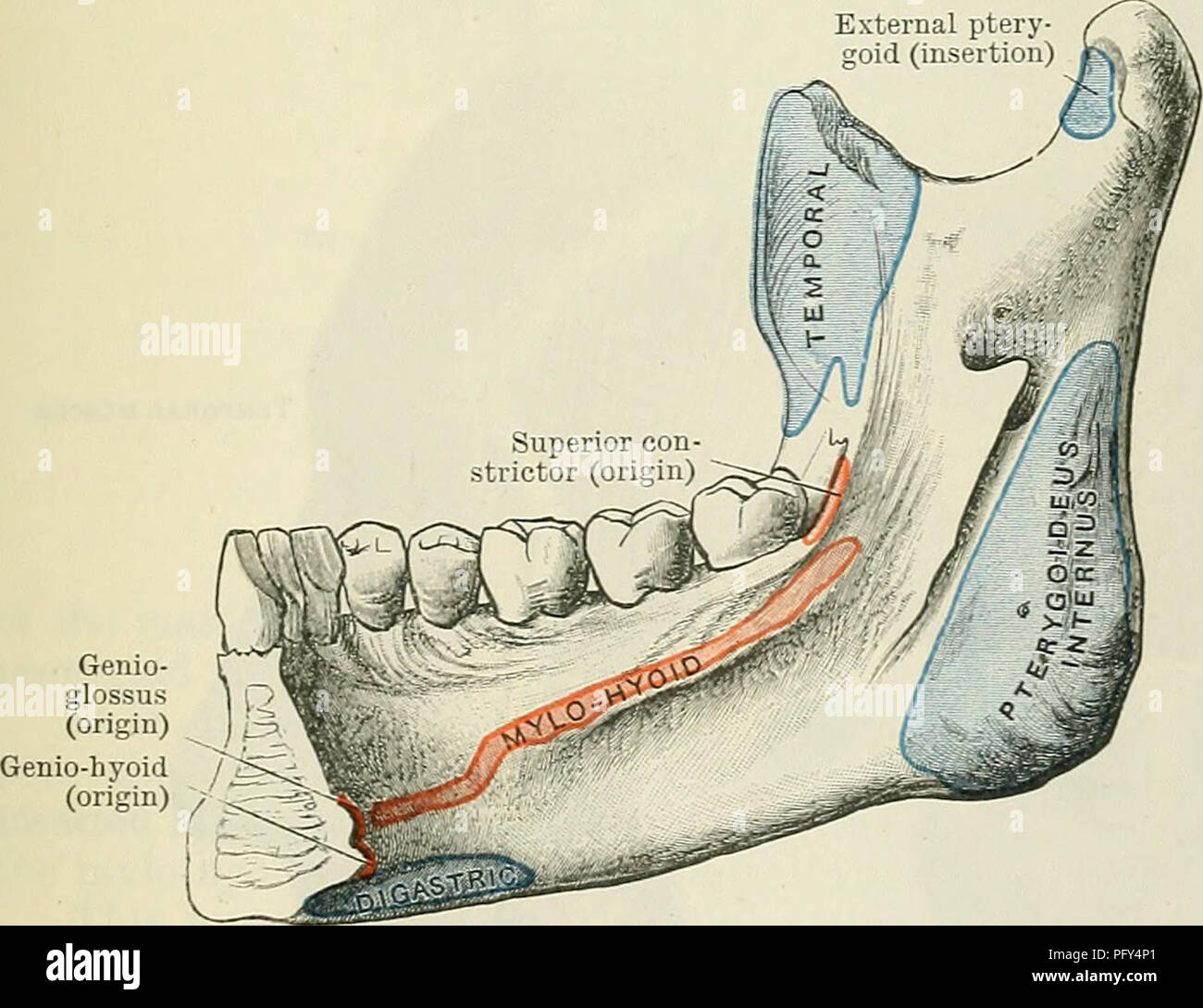
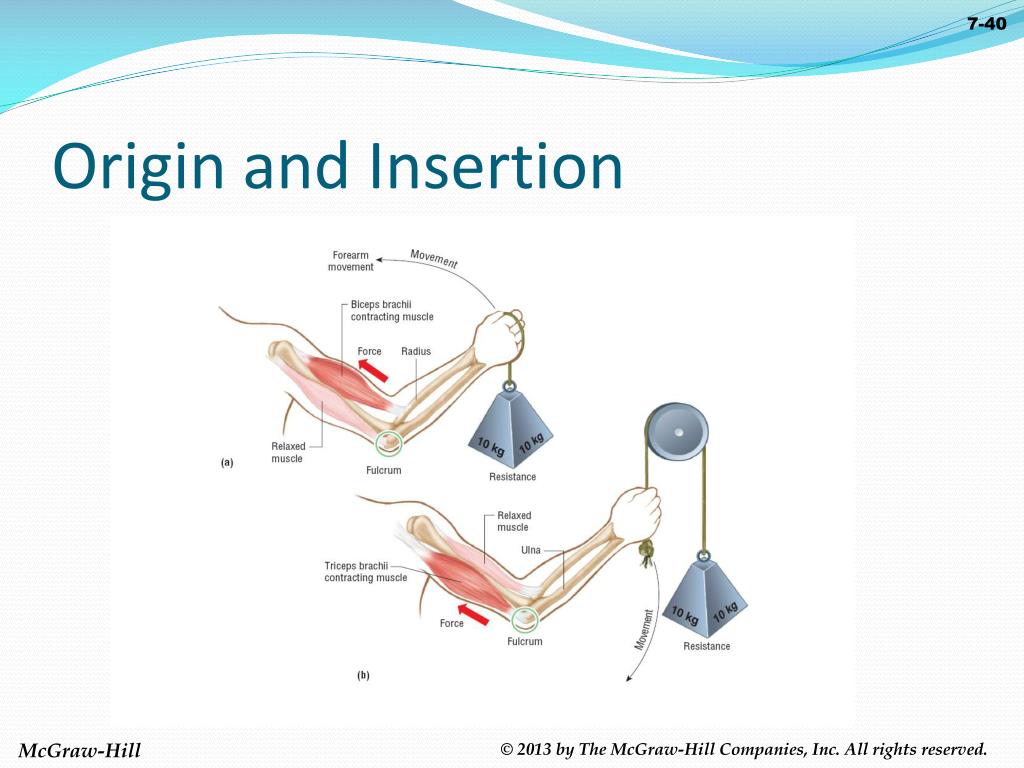
Define Insertion In Anatomy - The act or process of inserting. It is usually located distal to the. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move. Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are.
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. It is usually located distal to the. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. The act or process of inserting. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move.
Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The act or process of inserting. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move. It is usually located distal to the. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles.
Insertion Anatomy Definition Anatomy Drawing Diagram Muscle
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin.
Insertion Anatomy Definition Vastus Lateralis Muscle GetBodySmart
The act or process of inserting. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. It is usually located distal to the. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. The act or process of inserting. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
It is usually located distal to the. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move. Anatomy the point or.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. Well, let’s first define what.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. It is usually located distal to the. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move. In.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. Most often, the origin is defined as.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. Well, let’s first define what an origin and insertion are. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. The act or process of inserting.
Insertion Anatomy Definition
The act or process of inserting. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. Most often, the origin is defined as the attachment that stays fixed when a muscle. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension,.
Most Often, The Origin Is Defined As The Attachment That Stays Fixed When A Muscle.
The act or process of inserting. The main difference between origin and insertion is that origin is the attachment point of skeletal muscles, which does not move. When a muscle contracts, the insertion moves closer to the origin, facilitating movements like flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. In the world of anatomy, origin and insertion are crucial when discussing muscles.
Well, Let’s First Define What An Origin And Insertion Are.
It is usually located distal to the. The origin refers to the end of a muscle that. The insertion refers to the point where a muscle attaches to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts. Anatomy the point or mode of attachment of a skeletal muscle to the bone or other body part that it moves.